呼吸疾病国家重点实验室在人感染H5N6禽流感治疗研究取得新进展
导读
H5N6亚型禽流感病毒一般只在鸟类中感染并传播,但2014年以来,H5N6禽病毒在我国出现跨越种间屏障感染人事件。据世界卫生组织统计,迄今为止19例实验室确诊H5N6感染人病例,其中6人死亡,病死率约为32%。在2015年初,广州医科大学附属第一医院在全球首次成功救治了人感染H5N6患者。近日,呼吸疾病国家重点实验室在在小鼠动物模型中对广州H5N6人感染分离株病毒的致病性、体内复制特点、炎症反应进行了系统的研究。提示抗禽流感免疫球蛋白可用于救治H5N6感染者,降低死亡率。相关研究以“Patient-derived avianinfluenza A (H5N6) virus is highly pathogenic in mice but can be effectivelytreated by anti-influenza polyclonal antibodies”为题在线发表于国际学术期刊 Emerging Microbes & Infections上。

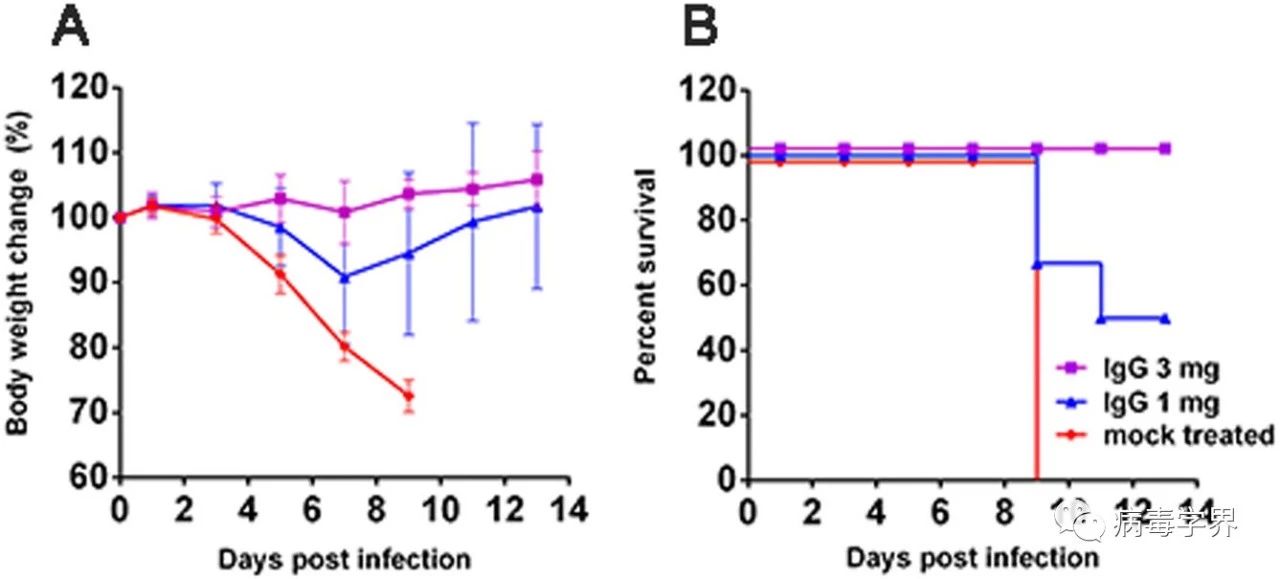
猕猴抗禽流感广谱免疫球蛋白对H5N6流感病毒感染小鼠的治疗效果
研究背景
甲型流感病毒依据病毒表面的血细胞凝集素(HA)和神经氨酸酶(NA)分为不同亚型,其中HA有18个亚型,NA有9个亚型。通常人类只感染甲流H1N1亚型、H3N2亚型和乙型流感病毒。H5N6亚型禽流感病毒一般只在鸟类中感染并传播,但2014年以来,H5N6禽病毒在我国出现跨越种间屏障感染人事件。据世界卫生组织统计,迄今为止19例实验室确诊H5N6感染人病例,其中6人死亡,病死率约为32%。2015年初,广州医科大学附属第一医院在全球首次成功救治了人感染H5N6患者。
结果速览
研究表明:
(1)H5N6人体分离株在小鼠具备高致病力,对小鼠的半数致死剂量仅为5 pfu,远高于报道的H5N1及H7N9禽流感病毒人感染分离株在小鼠的致病力。小鼠感染H5N6病毒后,病毒在多脏器快速复制并产生细胞因子风暴,导致小鼠迅速死亡。
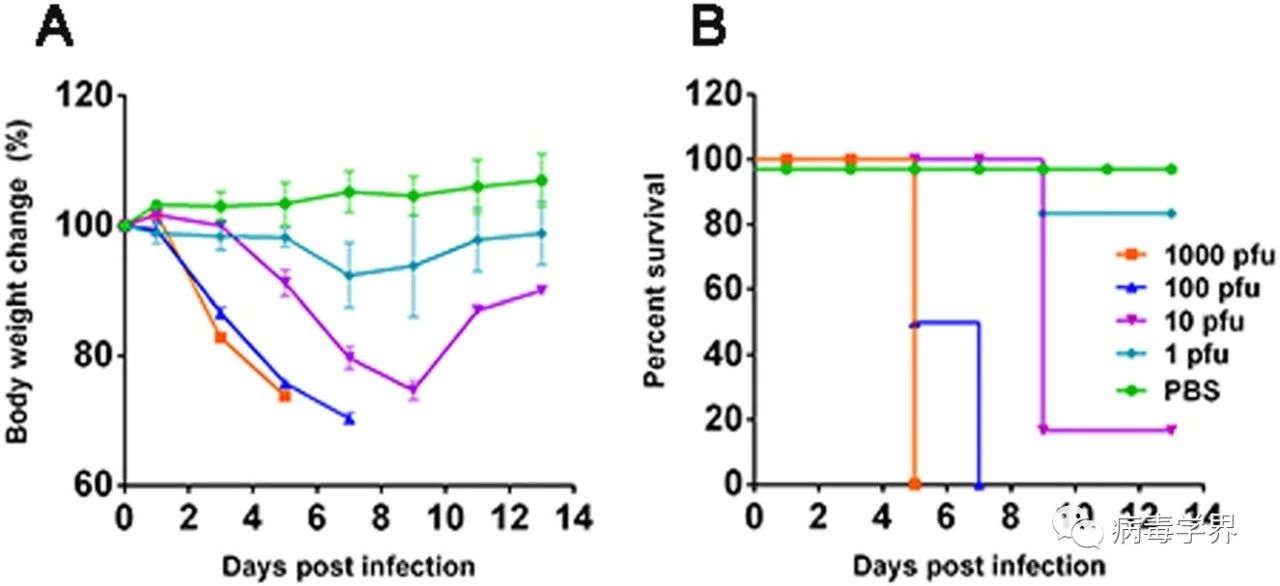
Fig. 1 Infection of the patient-derived H5N6/GZ14 isolate in mice
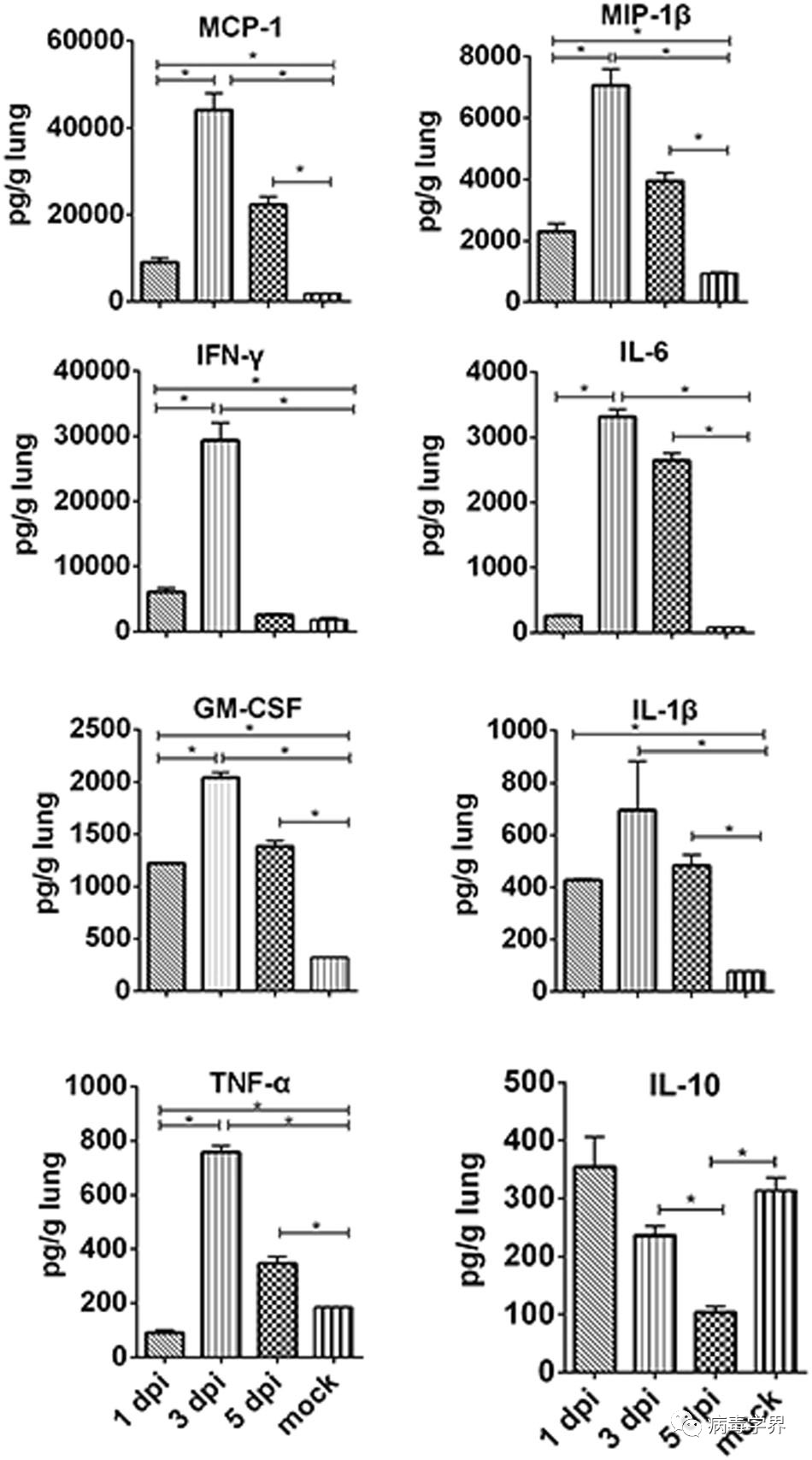
Fig. 2 Pro-inflammatory cytokines and chemokines in the lungs of H5N6/GZ14-infected mice
(2)研究人员使用实验室制备的猕猴抗禽流感广谱免疫球蛋白治疗,能够完全保护感染了致死剂量H5N6病毒的小鼠。该研究提示抗禽流感免疫球蛋白可用于救治H5N6感染者,降低死亡率。
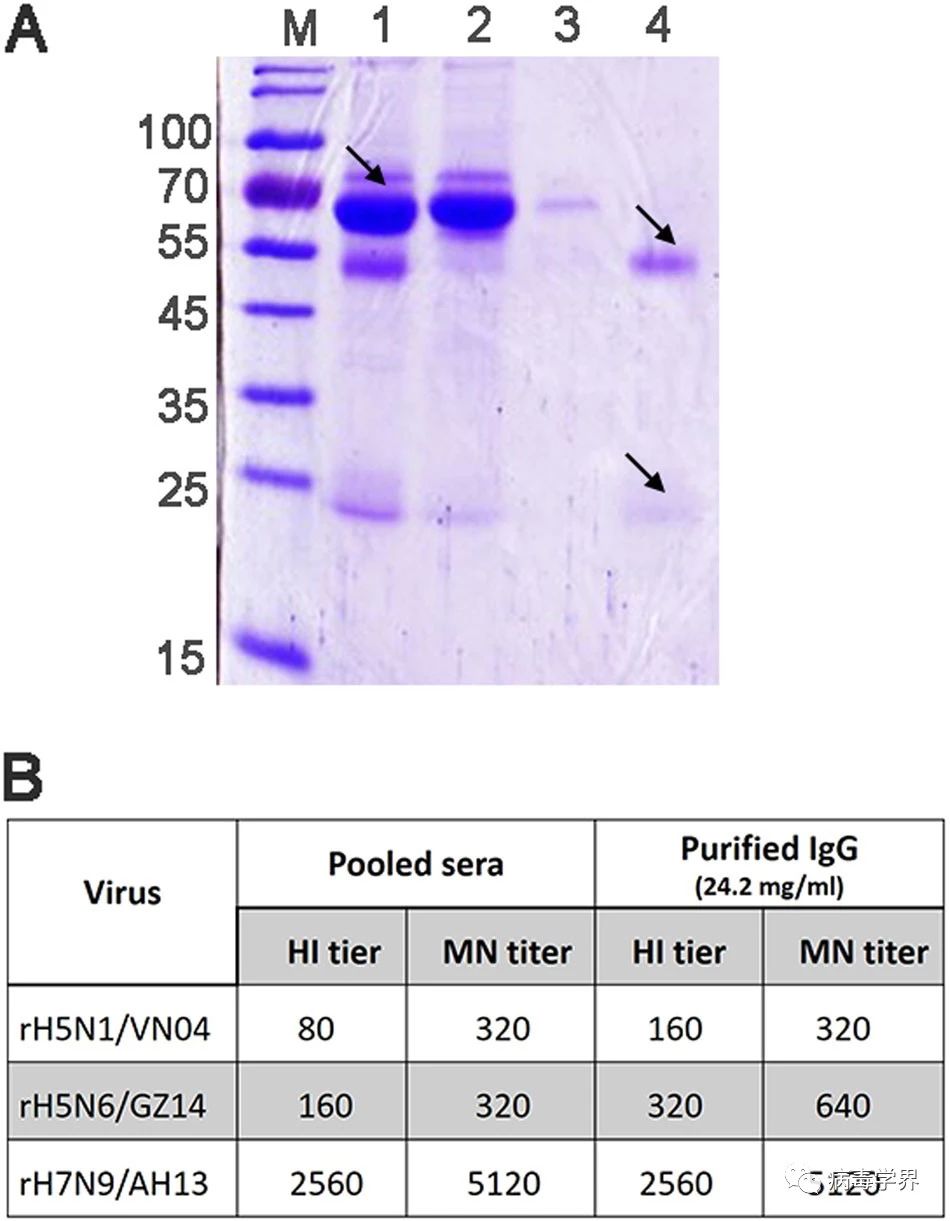
Fig. 3 Coomassie Blue staining after SDS-PAGE and the antibody titer of immunized rhesus macaque sera and purified IgG.
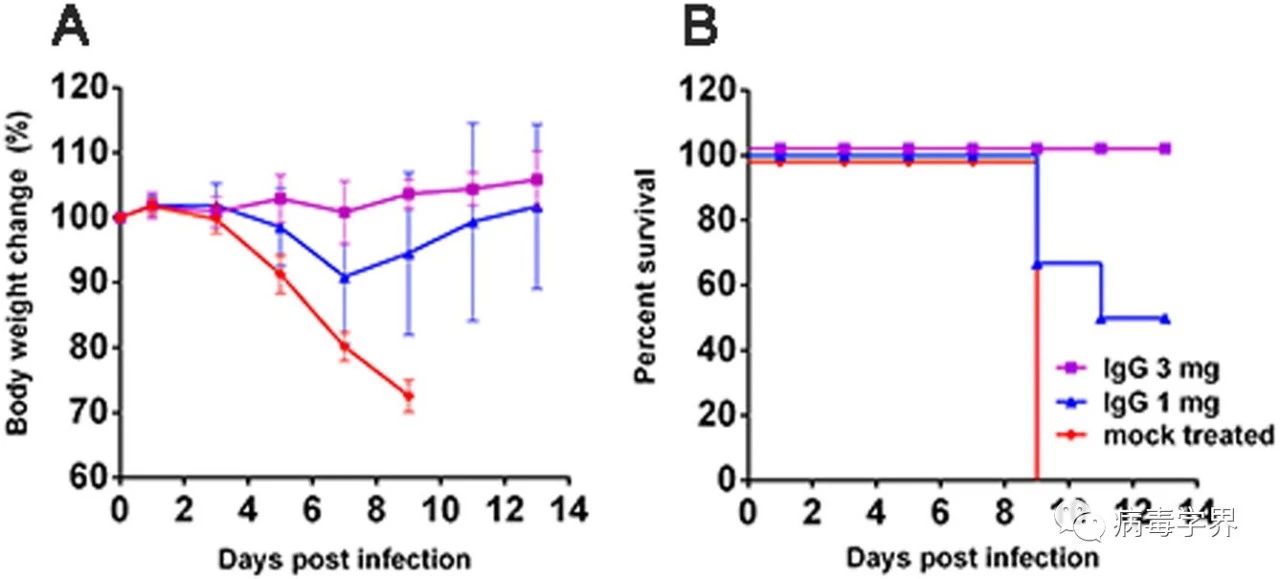
Fig. 4 Efficacy of anti-influenza polyclonal antibodies for treating H5N6/GZ14-infected mice
结语
本研究得到广州海关(原广东出入境检验检疫局)生物安全三级实验室的大力协助,国家自然科学基金、科技部H7N9应急专项、广州市健康医疗协同创新重大专项基金的经费支持。潘蔚绮副研究员和谢浩俊博士为该论文的共同第一作者,陈凌研究员和黄吉城研究员为该论文的共同通讯作者。
ABSTRACT
Highly pathogenic avian influenza A (H5N6) virus has been circulating in poultry since 2013 and causes sporadicinfections and fatalities in humans. Due to the re-occurrence and continuous evolution of this virus subtype, there is an urgent need to better understandthe pathogenicity of the H5N6 virus and to identify effective preventative and therapeutic strategies. We established a mouse model to evaluate the virulence of H5N6 A/Guangzhou/39715/2014 (H5N6/GZ14), which was isolated from an infected patient. BALB/c mice were inoculated intranasally with H5N6/GZ14 and monitored for morbidity, mortality, cytokine production, lung injury, viral replication, and viral dissemination to other organs. H5N6/GZ14 is highly pathogenic and can kill 50% of mice at a very low infectious dose of 5 plaque-forming units (pfu) Infection with H5N6/GZ14 showed rapid disease progression, viral replication to high titers in the lung, a strongly induced pro-inflammatory cytokine response, and severe lung injury. Moreover, infectious H5N6/GZ14 could be detected in the heart and brain of the infected mice. We also demonstrated that anti-influenzapolyclonal antibodies generated by immunizing rhesus macaques could protect mice from lethal infection. Our results provide insights into the pathogenicity of the H5N6 human isolate.
参考文献:
1. .Pan W, Xie H1, Li X, Guan W, Chen P,Zhang B, Zhang M1, Dong J, Wang Q, Li Z, Li S, Yang Z, Li C, Zhong N, Huang J,Chen L Patient-derived avian influenzaA (H5N6) virus is highly pathogenic in mice but can be effectively treated byanti-influenza polyclonal antibodies. Emerg Microbes Infect. 2018 Jun13;7(1):107.
doi: 10.1038/s41426-018-0113-2.
2. 呼吸疾病国家重点实验室:实验室人感染H5N6禽流感治疗研究取得进展
内容来源:病毒学界
卓诚惠生——国内多重PCR技术应用的开拓者
了解更多资讯,请识别下方二维码,关注卓诚惠生~
